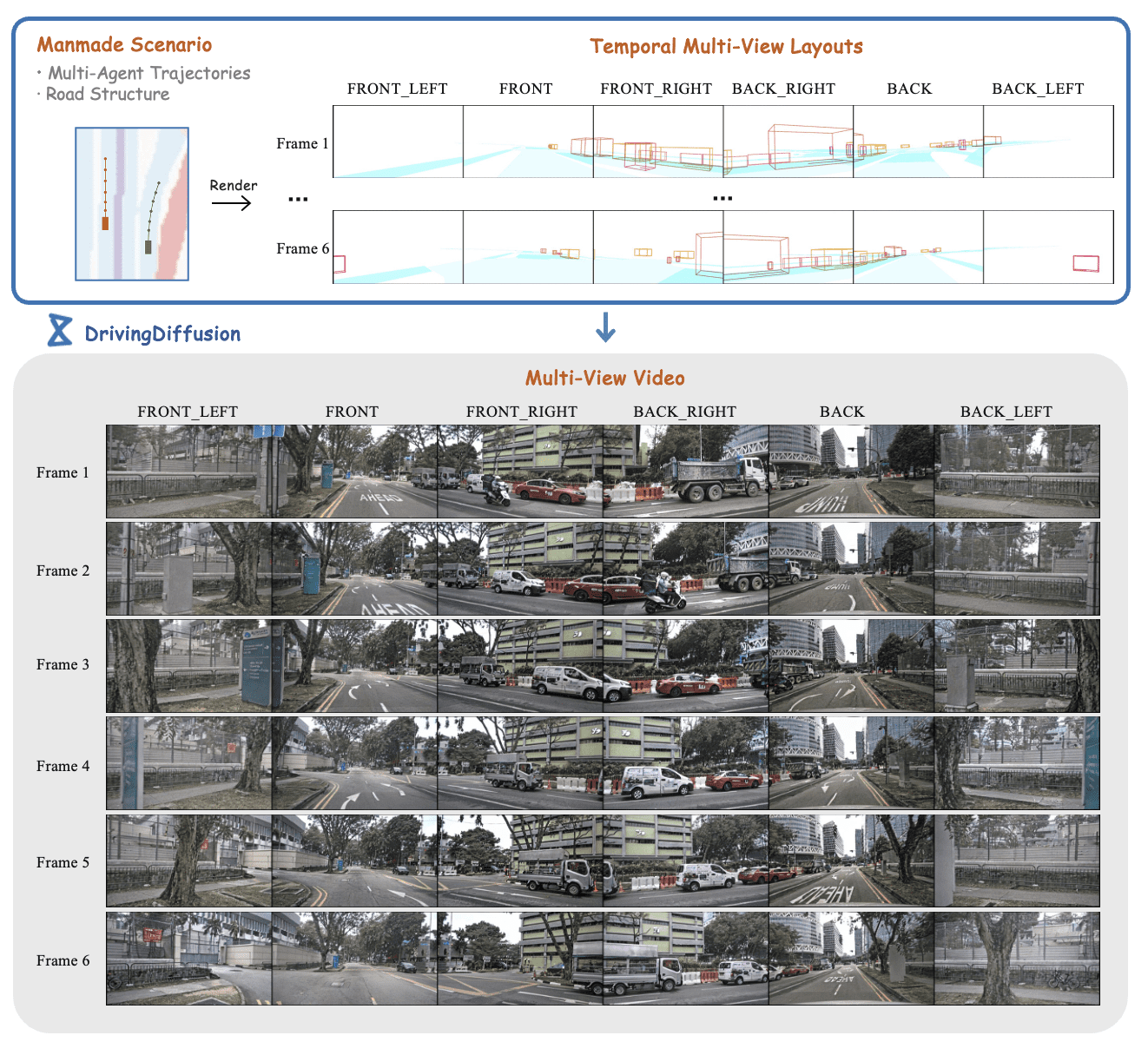
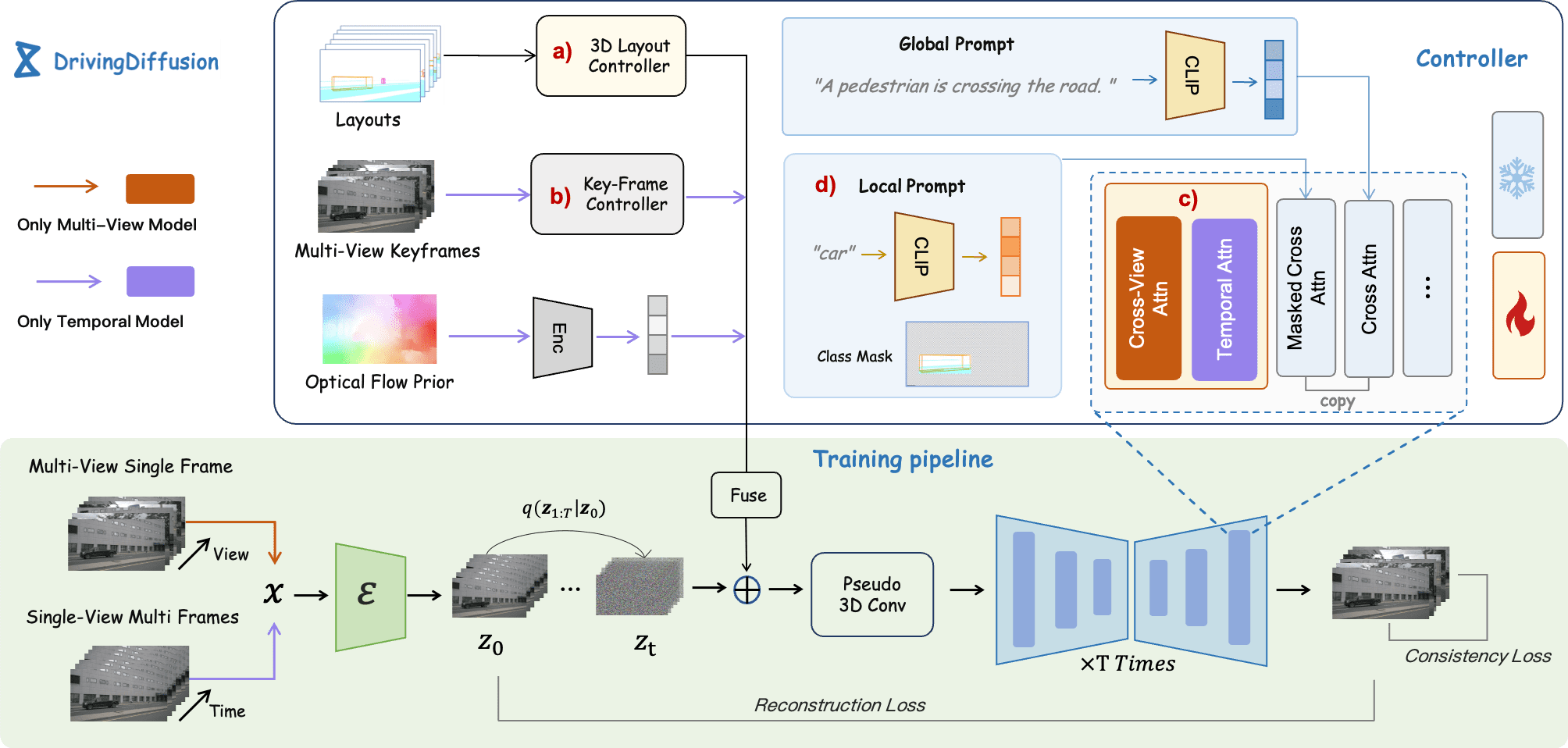
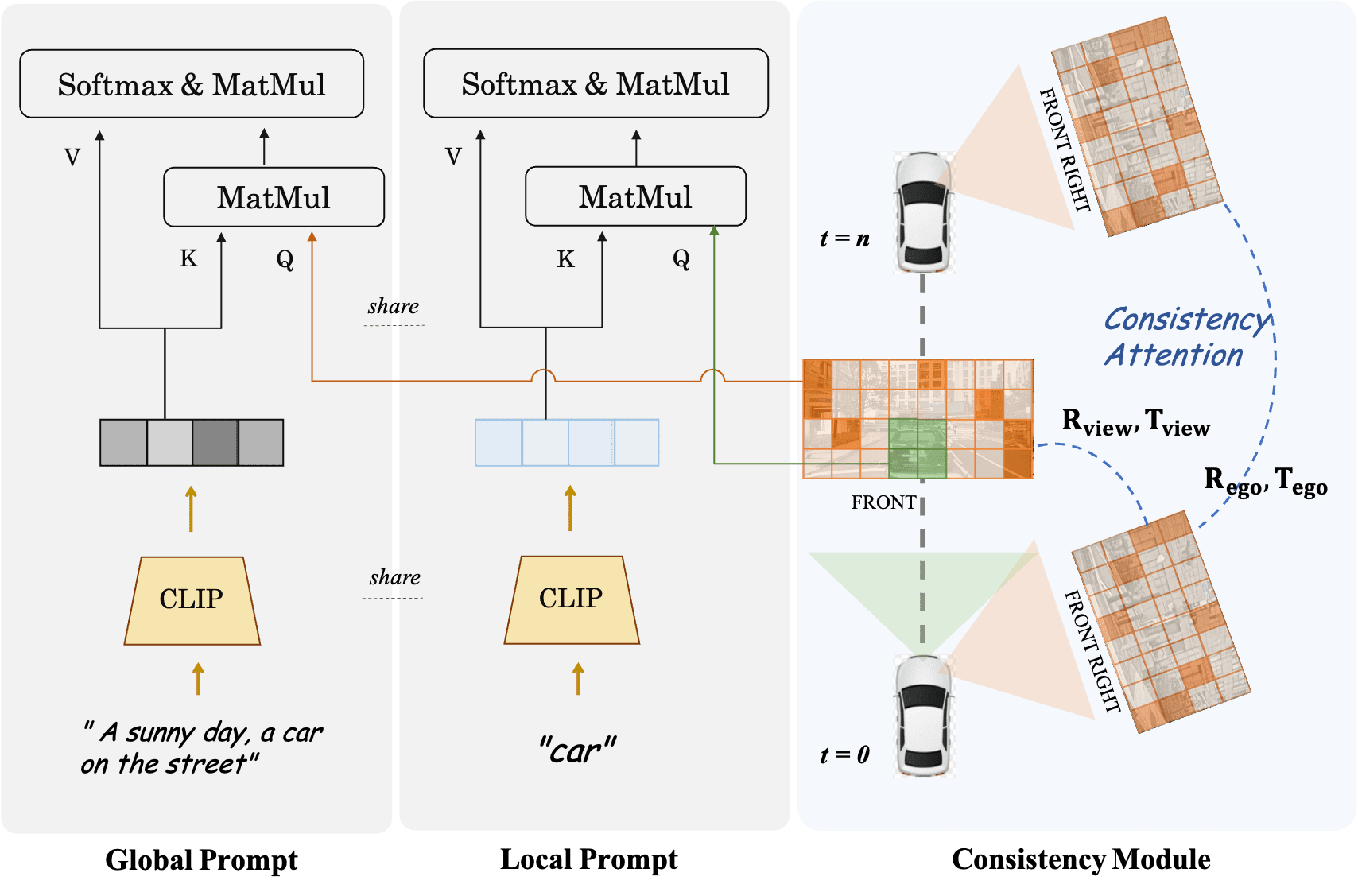
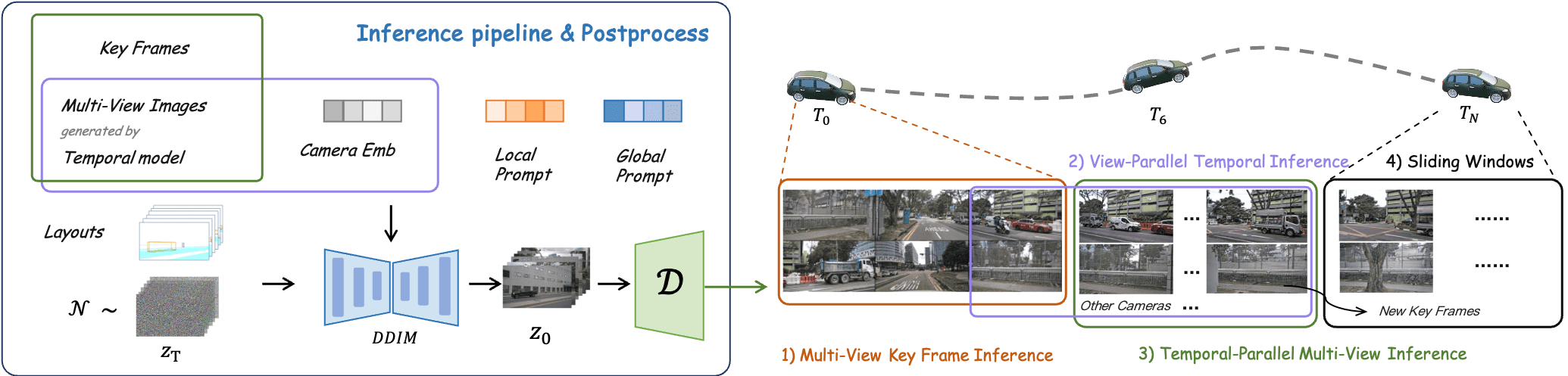
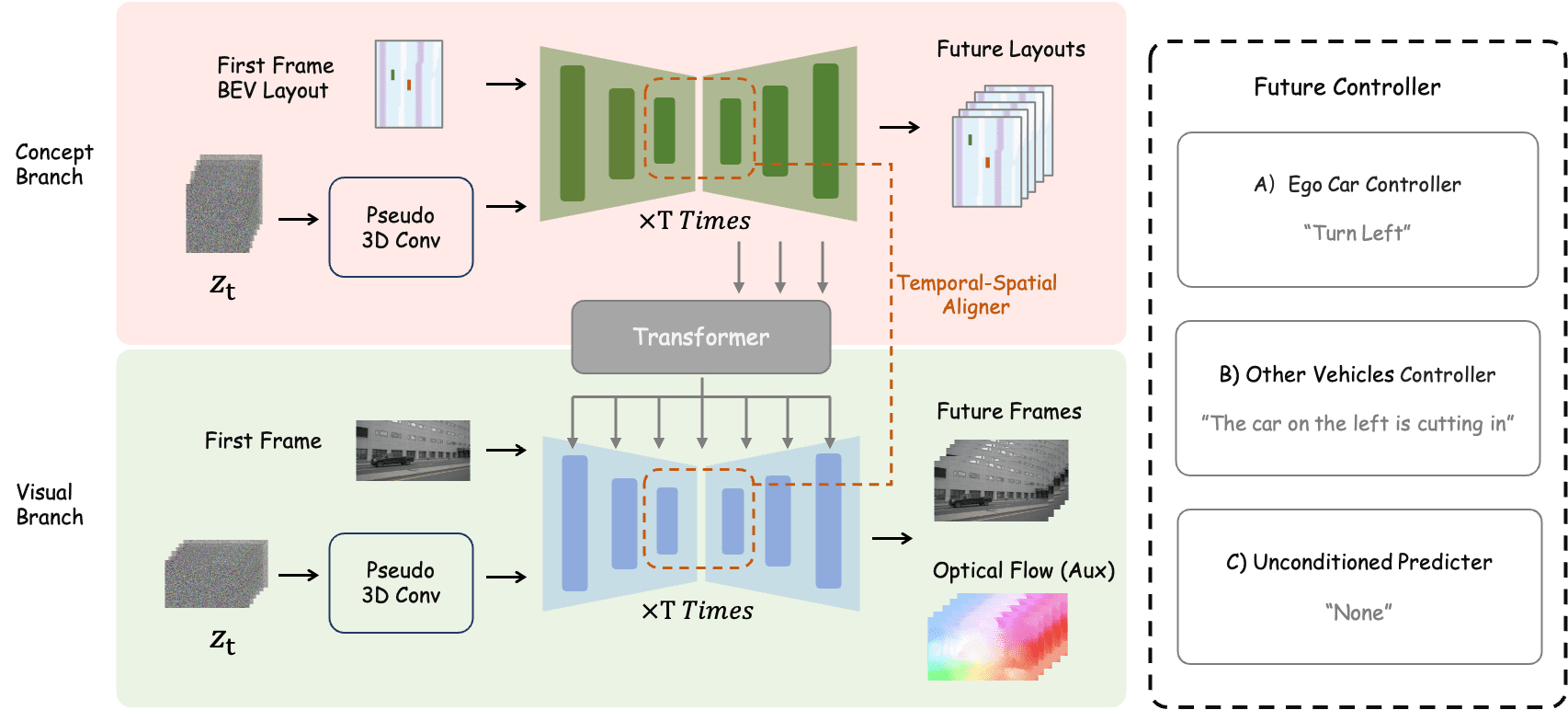
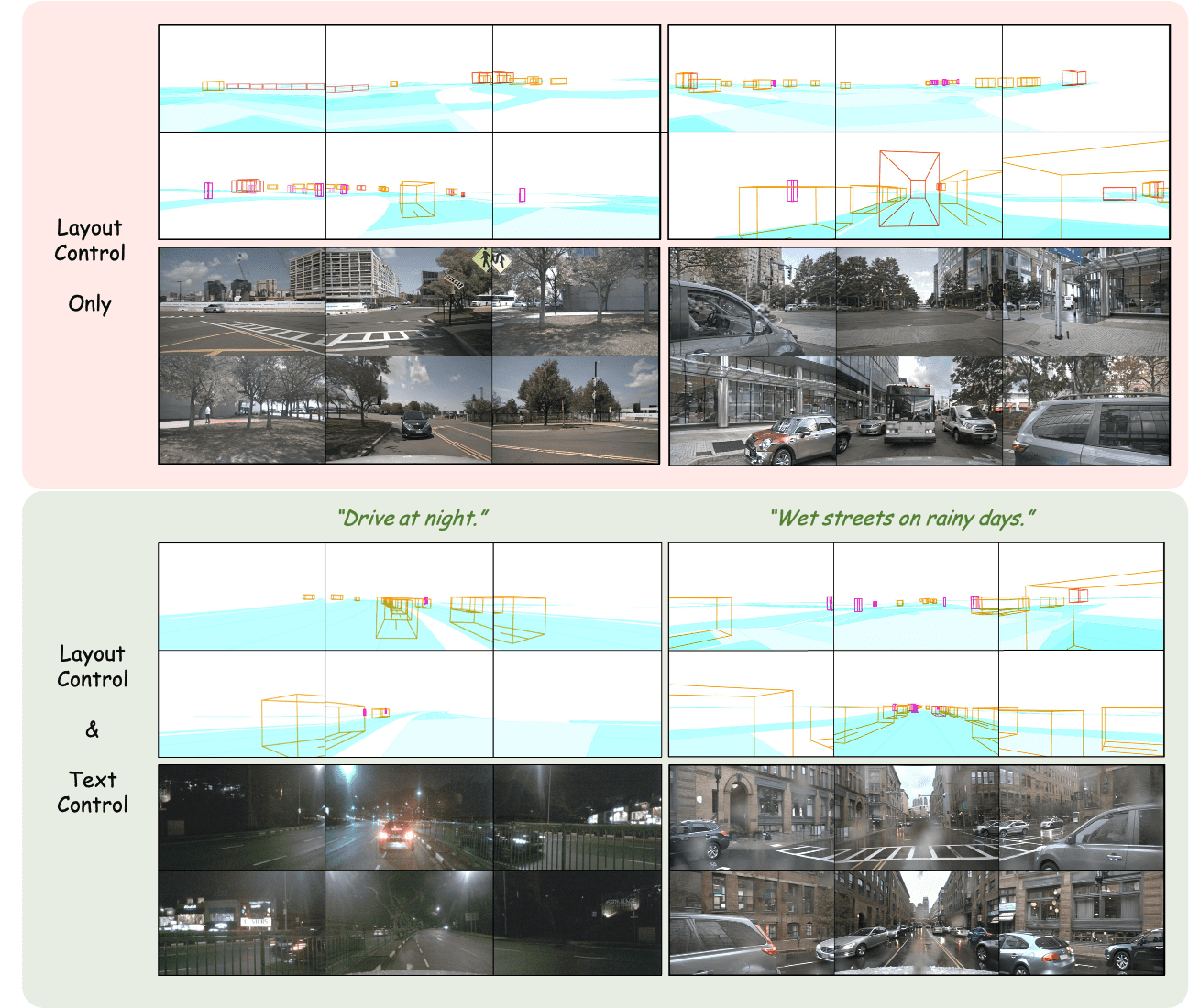
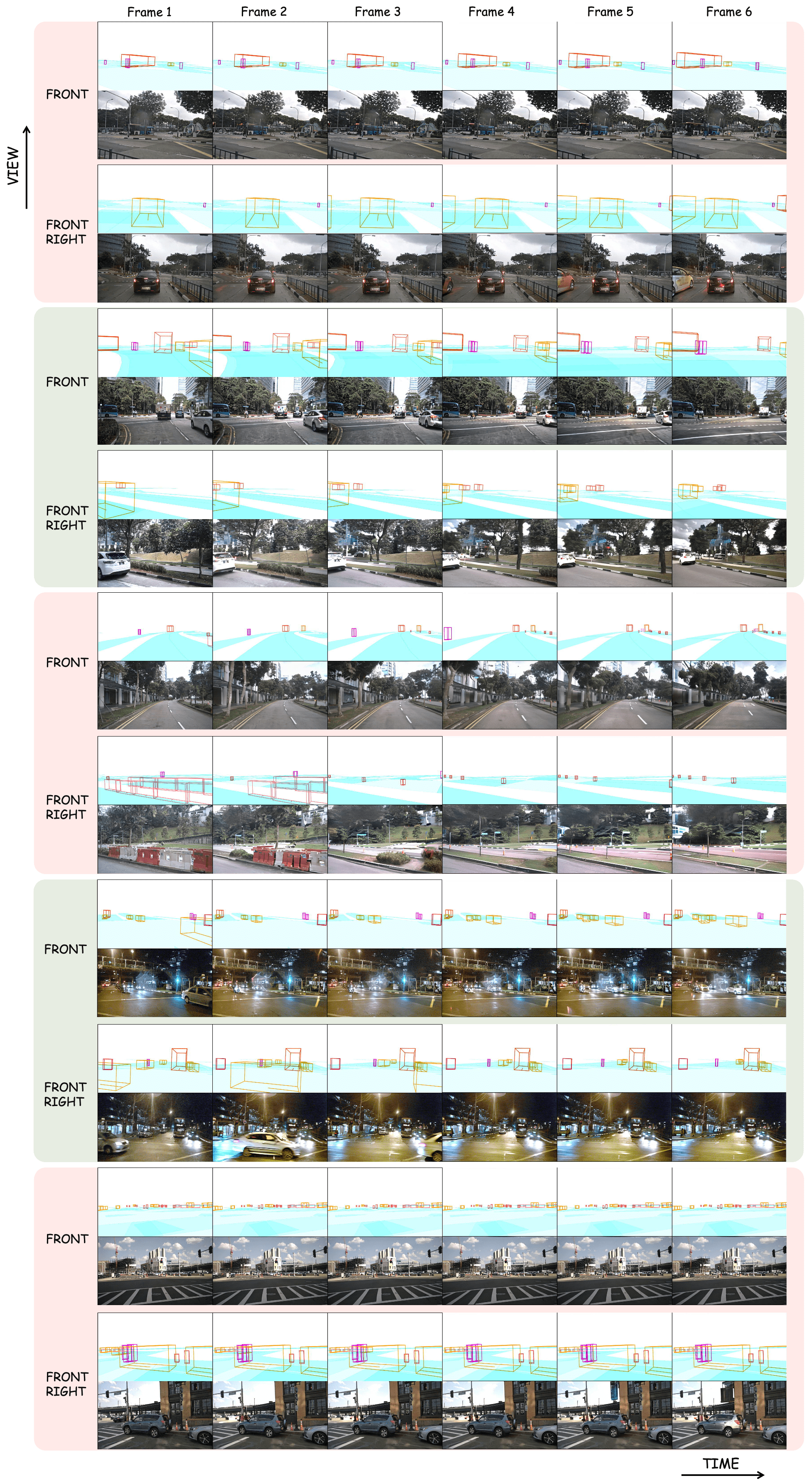
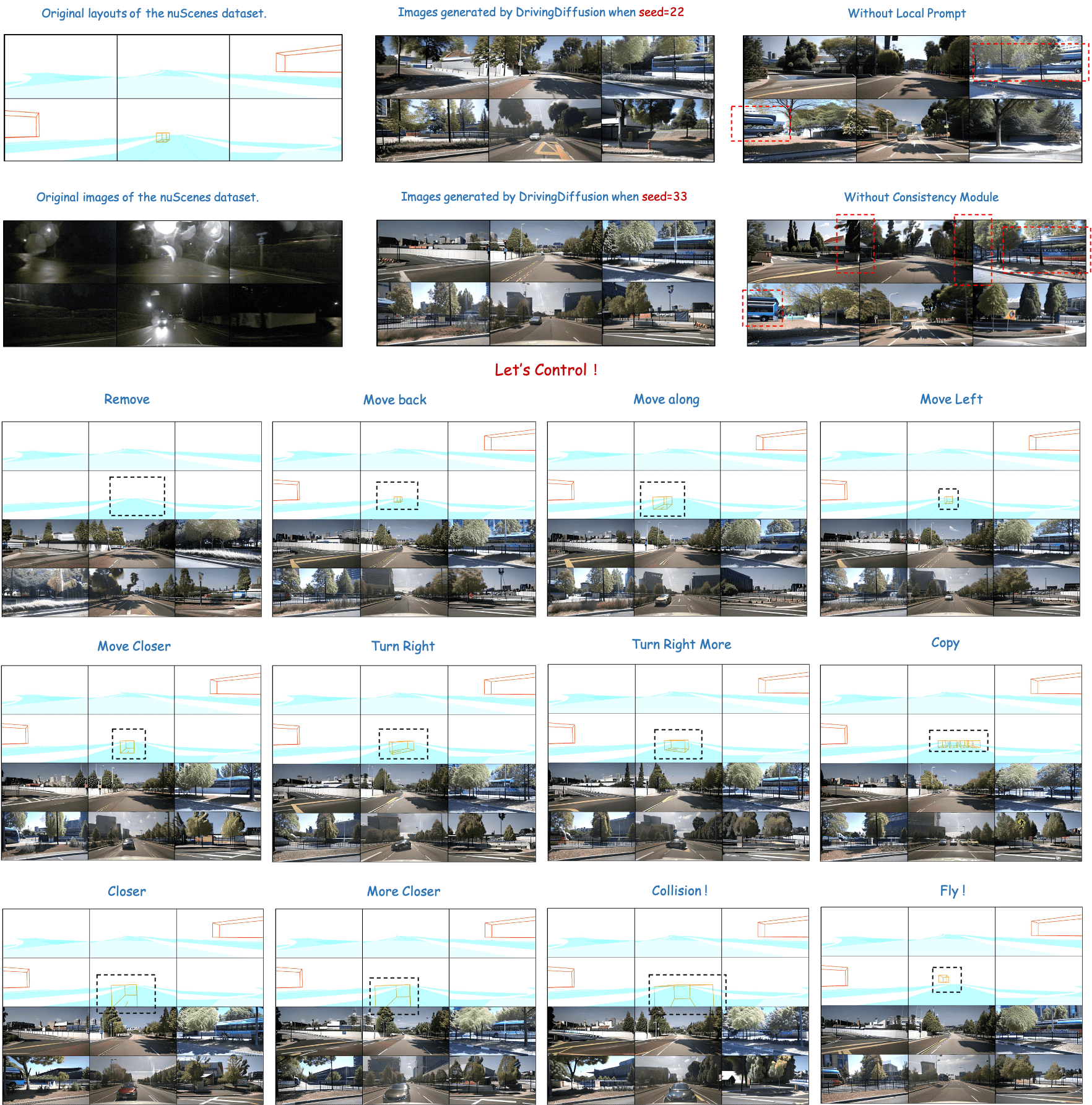
With the increasing popularity of autonomous driving based on the powerful and unified bird's-eye-view (BEV) representation, a demand for high-quality and large-scale multi-view video data with accurate annotation is urgently required. However, such large-scale multi-view data is hard to obtain due to expensive collection and annotation costs. To alleviate the problem, we propose a spatial-temporal consistent diffusion framework DrivingDiffusion, to generate realistic multi-view videos controlled by 3D layout. There are three challenges when synthesizing multi-view videos given a 3D layout: How to keep 1) cross-view consistency and 2) cross-frame consistency? 3) How to guarantee the quality of the generated instances? Our DrivingDiffusion solves the problem by cascading the multi-view single-frame image generation step, the single-view video generation step shared by multiple cameras, and post-processing that can handle long video generation. In the multi-view model, the consistency of multi-view images is ensured by information exchange between adjacent cameras. In the temporal model, we mainly query the information that needs attention in subsequent frame generation from the multi-view images of the first frame. We also introduce the local prompt to effectively improve the quality of generated instances. In post-processing, we further enhance the cross-view consistency of subsequent frames and extend the video length by employing temporal sliding window algorithm. Without any extra cost, our model can generate large-scale realistic multi-camera driving videos in complex urban scenes, fueling the downstream driving tasks. The code will be made publicly available.